In this article, we explain the difference between research method and research methodology. If you’re interested in a tool that helps you write & organize your research literature, click here to read more about Avidnote.
The main objective of research is to create new insight or develop a new theory. It is a very important aspect of education and life as a whole. This is why students at all levels of higher education are mandated to conduct research before they can graduate. The research process varies according to fields of knowledge. Research method and research methodology are terms often used interchangeably when carrying out research. But, strictly speaking, both terms are not exactly the same. The latter is a broader concept than the former.
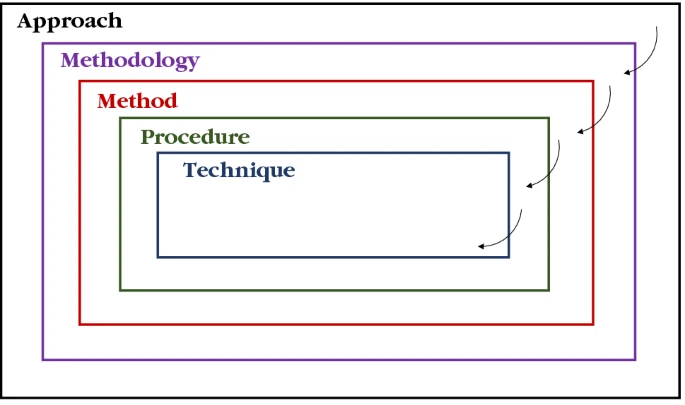
What is a research method?
A research method tries to describe those techniques or procedures which the researcher has deployed to answer the research questions, resolve the hypothesis, and ultimately solve the research problem, irrespective of whether the research belongs to the natura or social sciences or any other disciplines. It explains the procedures used to collect data as well as the techniques for data analysis, among others.
In other words, a research method explains how a researcher identifies, collects, processes, and analyzes data for his paper. A cogent explanation of these procedures and techniques is necessary because it allows readers to critically examine the overall validity and reliability of the empirical findings of the paper. The main purpose of a research method is to provide the scientific steps that help to find solutions to the research problem.
In short scientific papers [such as journal articles] which aim to report specific findings, the paper format often includes a “Methods section” that presents all the techniques and procedures used to identify, collect, process/measure, and analyze data/information for their paper.
The methods can be classified into three groups.
- Group one includes methods that focus on collecting and describing data
- Group two includes a collection of techniques meant to help establish a statistical relationship between variables;
- Group three is made up of methods used to evaluate the reliability, validity, and accuracy of the results of the processed or measured data.
Research methods can be qualitative and quantitative in nature. A combination of both methods is knows as mixed methods research. Mixed approaches can be undertaken if the researcher seeks to triangulate using different data sources. Triangulation refers to the act of using multiple methods or sources for data in qualitative research in order to gain a more comprehensive understanding of a phenomena (Patton, 1999). It provides you with a qualitative research strategy to test validity through the convergence of data from various sources.
Qualitative methods
In qualitative methods, data is not collected and processed numerically but mostly in words or literature. Qualitative research tries to investigate people’s comprehension of their social reality. It is inspired by many philosophical tenets and seeks to inquire about the diverse facets of human life, for example, culture, beliefs, morality, etc. It is part of the curriculum in several disciplines such as the arts, psychology, anthropology, and others. Some ways of collecting qualitative data include observation (including participant observation), interviews, questionnaires, documentary sources focus groups, artifacts, audio and visual materials, among others.
Qualitative data can be analyzed through transcription, coding, historical and philosophical literature analysis. Subjectivity in data collection and analysis can be a problem in qualitative analysis.
Quantitative methods
Quantitative research methods attach more importance to the use of numeric values when collecting, measuring, analyzing, and interpreting data. Researching with quantitative methods can help find patterns and averages, test causal relationships, forecast future patterns/trends, and generalize sample results to larger populations. It relies heavily on the use of statistical methods and principles. Software products like SPSS, STATA, and Eviews are designed to work with quantitative data.
There are different kinds of quantitative research. Some of them include experiments, surveys, interviews, etc.
What is a research methodology?
Whenever a researcher chooses any particular research method, he or she must justify or rationalize why such a method is preferred to others. Research methodology seeks to answer this question. Research methodology refers to the underlying logic or reasons behind the choice of methods for a research project. It involves studying the methods used in any particular field as well as the views, beliefs, values, theories, or principles behind their adoption in order to develop an approach that matches the objectives of the research.
In other words, research methodology is the rigorous analysis and evaluation of the methods applied in conducting research to ensure that the conclusions drawn are valid, reliable, and credible. Hence, research methods can be said to be a component of research methodology.
Longer or more complex research projects such as dissertations or theses will most likely include a “Research methodology” chapter where the researcher carefully explains the techniques and procedures he or she used to answer the research questions, test the hypothesis and solve the research problem.
For research whose methodology includes an interview or questionnaire, some crucial questions that arise include:
- Was the research instrument designed appropriately?
- Why was the instrument selected?
- Was it scrutinized for validity and reliability?
- Is it appropriate for addressing the research hypothesis, questions, and problem?
- What informed the chosen sample?
- Is the sample size representative of the overall population?
- What determined the choice of techniques for analyzing data?
Distinguishing between research method and research methodology
| Research Method | Research Methodology |
| The techniques and procedures used in solving research problems | The study of research methods in other to logically justify why any particular method should be preferred to others |
| The major aim is to solve the research problem | The major aim is to ensure that appropriate methods are used to solve research problems |
| Is a component of research methodology and hence narrower in scope | Encompasses both research methods and the logic behind their adoption and hence broader in scope |
| Involves the use of quantitative and qualitative research methods and utilizing the knowledge and skills learned through research methodology. | Involves the learning of various techniques to conduct research and acquiring methodical knowledge to perform quantitative, qualitative, and mixed research. |
✅ Also check out
This post was produced as part of a research guide series by Avidnote which is a free web-based app that helps you to write and organize your academic writing online. Click here to find out more.
Sources:
Andiappan, V., Wan, Y.K. Distinguishing approach, methodology, method, procedure and technique in process systems engineering. Clean Techn Environ Policy 22, 547–555 (2020).
Patton, M.Q., 1999. Enhancing the quality and credibility of qualitative analysis. Health services research, 34(5 Pt 2), p.1189.


